_1730972427_WNo_1600d900.webp)
In the context of continuous upgrades to global power infrastructure, pigtail bolts serve as critical fasteners connecting power lines to utility poles, and their selection and installation quality directly affect the safety and stability of distribution networks. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission, a significant proportion of power line failures are related to fastener failures, and high-quality pigtail bolts can significantly reduce such risks. This guide systematically introduces the design principles, technical specifications, application scenarios, and installation best practices of pigtail bolts to help engineers, procurement personnel, and project managers make informed decisions.
Pigtail bolts are indispensable specialized fasteners used in the construction of transmission and distribution line poles and towers, widely applied in power lines, communication lines, and various outdoor infrastructure projects. This special fastener, with its unique "pigtail" shaped design, provides flexibility that traditional bolts cannot achieve in confined spaces or special angle installation conditions. With the continuous growth of global renewable energy generation capacity and the acceleration of smart grid construction, the demand for high-quality pigtail bolts is steadily increasing.
However, how to find high-quality, durable, and reliable pigtail bolts among the numerous products on the market remains a challenge for many project managers. Substandard fasteners can lead to line sagging, structural damage to poles, and even safety incidents, causing huge economic losses and social impacts. This guide will deeply explore all key aspects of pigtail bolts, including design characteristics, technical specifications, material selection, manufacturing processes, and best practices for installation and maintenance, helping you gain a comprehensive understanding of this important power infrastructure component.
A pigtail bolt is a specialized fastener designed for various pole and tower line installations, characterized by its unique "pigtail" shaped end. This distinctive design makes it a critical component in power line pole and tower construction, providing reliable connection solutions in space-restricted or angle-special installation environments. Pigtail bolts are typically used in conjunction with insulators, clamps, and hangers, forming a complete line fixing system.
Power Transmission
HV/LV line construction & maintenance
Telecom Engineering
Fiber optic cable & pole line fixing
Construction
Signage & lighting equipment installation
Industrial Facilities
Equipment brackets & pipeline fixing
Professional Tip: When selecting pigtail bolts, consider load requirements, environmental conditions, and installation space limitations based on the specific application scenario. For long-term outdoor applications, it is recommended to prioritize hot-dip galvanized or stainless steel products and conduct regular maintenance inspections.
A complete pigtail bolt kit typically consists of the following core components, each performing specific functions to ensure the reliability of the entire connection system.
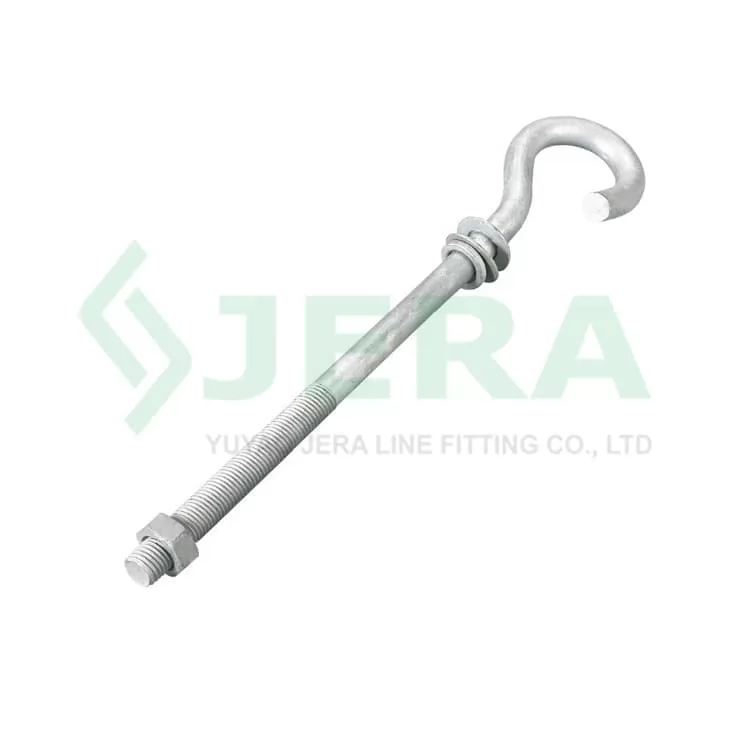

Typical Pigtail Bolt Component Structure
Pigtail bolts are known by various names in different regions and industries, including pigtail eye bolt, pigtail hook, pigtail screw, pigtail hook screw, and pigtail fastener. From a functional definition perspective, it belongs to a special form of pigtail hardware products, specifically designed for power line and communication line fixing installations.
Pigtail bolt designs are not uniform; different countries and regions have developed various structural variants based on local usage habits and standards, each with specific advantages and application scenarios.
| Design Type | Main Features | Applicable Regions | Unique Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welded Washer Type | Square or round washer welded to the pigtail hook neck | Kenya, Zambia, and other African countries | Integrated washer and bolt, high installation efficiency |
| Forged Position Type | Two forged protrusions on left and right sides of neck | Malaysia and other Southeast Asian countries | Prevents washer detachment, suitable for vibration environments |
| European Standard Type | Complies with EN 50182 and other European standards | EU member states | High standardization, excellent interchangeability |
| American Standard Type | Complies with ASTM standards | North America | High thread accuracy, strong load capacity |
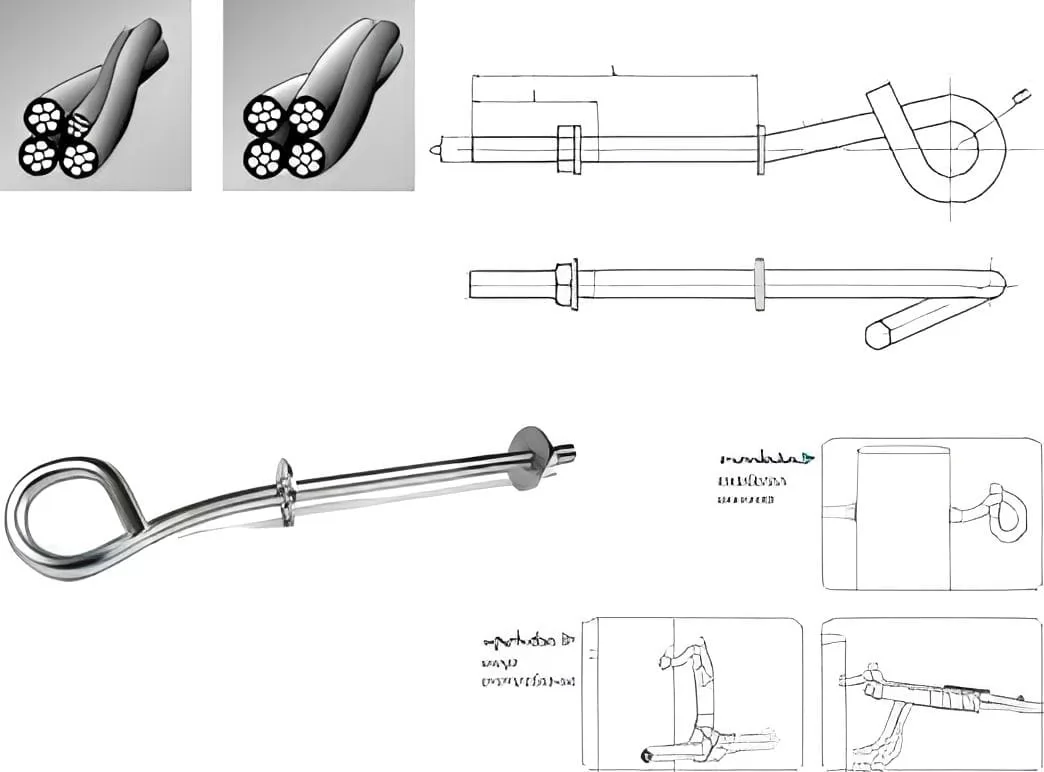
Pigtail bolts are typically made of metal materials, with a threaded portion similar to ordinary bolts, but the curved end provides additional flexibility. This curved design allows it to adapt to confined installation spaces or specific installation angles, which is the core advantage of pigtail bolts compared to traditional straight bolts. The curved end design has been optimized for mechanics, effectively distributing loads and reducing stress concentration, thereby improving the reliability of the entire connection system.
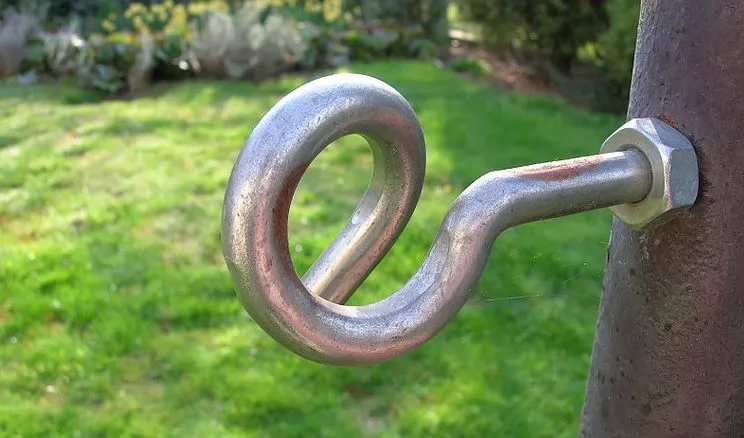

Load Transfer Path
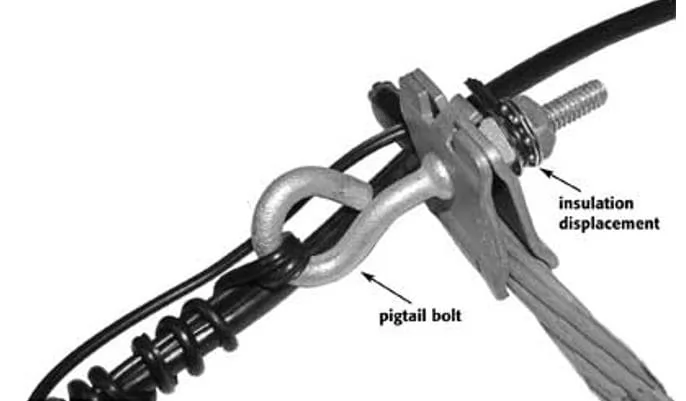
Typical Installation
_1730971841_WNo_975d508.webp)
Dimension Drawing
Pigtail bolts achieve reliable connection and fixation through their unique design. The working principles can be understood from the following aspects:
Power engineering is the primary application area for pigtail bolts, with their presence ranging from high-voltage transmission lines to low-voltage distribution networks. Applications in power systems can be divided into the following specific scenarios.
Safety Notice: Power line installation is a special operation that must be performed by qualified professionals. Incorrect installation may cause serious personal injury and equipment damage. Please strictly comply with local safety regulations and operating procedures.
The rapid development of the telecommunications industry has created broad application space for pigtail bolts. From traditional communication pole lines to modern 5G base station infrastructure, pigtail bolts play important fixing roles.
In fiber optic communication networks, pigtail bolts are used for the routing and fixing of optical cables on pole lines. Compared to traditional copper cables, optical cables have lighter weight and better flexibility, but also place higher requirements on fixing points. The curved design of pigtail bolts can effectively support the routing of optical cables, preventing signal attenuation caused by excessive bending at fixing points. In 5G base station construction, miniaturized base station equipment often needs to be installed on existing towers, building exteriors, or street light poles. The flexibility of pigtail bolts makes them an ideal choice for such applications.
In addition to the two main application areas of power and telecommunications, pigtail bolts also have wide applications in construction and manufacturing industries.
Case Study: In a large commercial complex project, the construction party used more than 500 sets of pigtail bolts for various signage and wayfinding system installations. The project manager stated that compared to traditional expansion bolts, pigtail bolts showed obvious advantages in installation efficiency and long-term reliability.
In construction engineering, pigtail bolts are commonly used for outdoor signage systems, lighting fixtures, surveillance cameras, and other facility installations and fixing. Their curved end design allows for flexible angle adjustment without compromising structural strength, which is particularly useful for equipment installations requiring precise alignment. In the manufacturing sector, pigtail bolts can be used for various mechanical equipment bracket fixing and pipeline support applications. Due to their good versatility and economy, pigtail bolts have become common parts in industrial maintenance and equipment renovation projects.
Compared to traditional fasteners, pigtail bolts have multiple unique advantages that make them irreplaceable in specific application scenarios.
Pigtail bolts provide more stable connections in complex installation environments, especially suitable for structures requiring additional support
The unique design helps distribute pressure, extending service life with minimal deformation over long-term use
Suitable for confined spaces or special angle installations, adapting to various complex environments
Special design simplifies installation process, significantly reducing time for complex connections
Able to accommodate minor dimensional variations, reducing installation precision requirements
Correct installation is key to ensuring pigtail bolts perform at their best. Below we provide detailed introductions to the complete installation process, solutions to common problems, and best practices for maintenance.
Step 1: Confirm Correct Component Selection
Before starting installation, it is essential to select the appropriate pigtail bolt component specifications based on specific application requirements. Selection should comprehensively consider:
Step 2: Inspect All Components
Before installation, all components should be carefully inspected to ensure:
Step 3: Install Washers
First, install the first washer onto the shaft of the pigtail bolt. If the application requires anti-loosening function, install a spring washer (lock washer) after the first washer, followed by the second regular washer. This combined installation method effectively distributes loads and prevents nut loosening during use, and is standard practice for power line installations. Washer selection should match the bolt specification; washers that are too large or too small will affect connection effectiveness.
Step 4: Pass Through Installation Hole
Pass the curved end of the pigtail bolt through the pre-drilled installation hole. During passage, ensure the first washer is tightly fitted between the bolt curved section and the pole surface. This step is crucial for establishing firm initial contact between the bolt and the pole. The installation hole diameter should be 1-2mm larger than the bolt shaft diameter to ensure smooth passage and allow for adjustment tolerance.
Step 5: Install Second Washer
After the pigtail bolt completely passes through the installation hole, install the second washer on the exposed bolt shaft. This washer's function is to distribute fastening force on the other side of the pole, ensuring even and secure connection. Dual-washer installation is standard practice for pigtail bolt installations, effectively protecting pole materials from crushing while improving connection stability.
Step 6: Install and Tighten Nuts
In clockwise direction, screw the two hex nuts onto the pigtail bolt shaft. First, hand-tighten the first nut against the washer. Then use an appropriately sized wrench to tighten both nuts in a cross-pattern sequence. During tightening, pay attention to controlling torque to avoid overtightening causing bolt stretching deformation, washer damage, or pole material cracking. Recommended tightening torque should be determined based on bolt specification and material, generally referencing relevant industry standards.
| Bolt Specification | Thread Type | Recommended Torque (N·m) | Applicable Pole Types | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M12 | Metric Coarse | 45-55 | Wood, Concrete | General Applications |
| M16 | Metric Coarse | 110-130 | Wood, Concrete | General Applications |
| M18 | Metric Coarse | 150-180 | Concrete, Steel | Heavy Load |
| M20 | Metric Coarse | 210-250 | Concrete, Steel | Heavy Load |
| 5/8" UNC | Imperial Coarse | 80-100 | Wood | North American Standard |
| 3/4" UNC | Imperial Coarse | 140-170 | Wood, Concrete | North American Standard |
| Common Problem | Possible Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nut Loosening | Vibration, insufficient torque, no lock washer | Retighten and add spring washer or use lock nut | Use double-nut locking, regular inspection |
| Bolt Bending Deformation | Overload, impact load, improper angle | Replace with higher load rated bolt | Select correct load rating, avoid lateral forces |
| Washer Crushing | Excessive torque, mismatched washer size | Replace with correct washer size, use recommended torque | Use matching washers, control tightening force |
| Thread Stripping | Thread damage, insufficient lubrication, forced installation | Replace bolt, clean threads and apply lubricant | Inspect threads before installation, use proper lubrication |
| Coating Peeling | Mechanical damage, improper handling | Repair with zinc-rich paint, replace if severe | Handle carefully, avoid impact damage |
Maintenance Inspection Checklist:
Regular maintenance inspection is an important measure to ensure long-term reliable operation of pigtail bolts. Inspection and maintenance are recommended according to the following cycles:
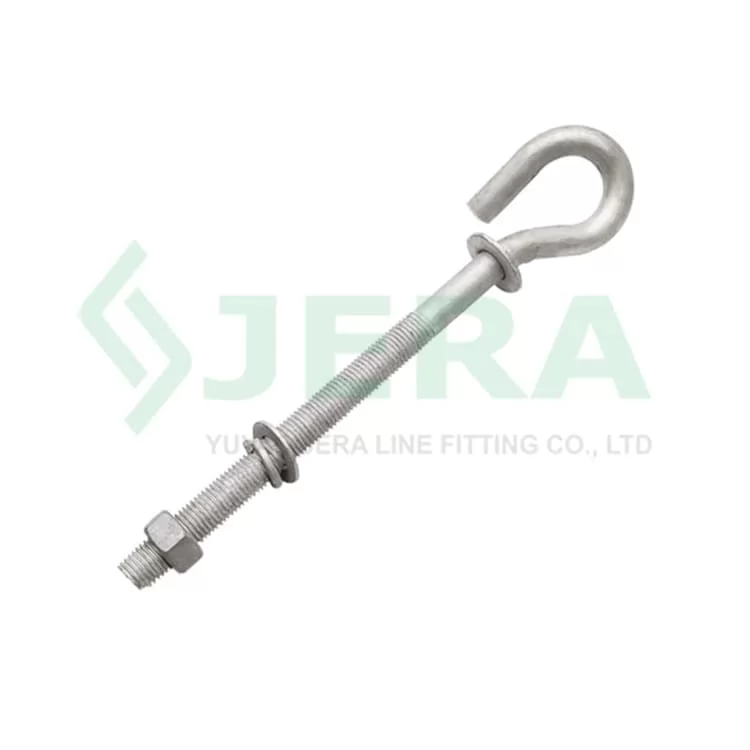

Pigtail Pole Bolt · LV Line Special
Pigtail Pole Bolt PB-16-300 (also called pigtail anchor bolt) is specifically designed for wooden, concrete, or other power line poles for hanging and tensioning low-voltage dead-end clamps or suspension clamps.
Low-voltage power cable line distribution systems, urban grid renovation, rural grid upgrades, renewable energy station collection lines
| Product Code | MBL (kN) | Weight (kg) | Material | Diameter × Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB-12-200 | 10 | 0.52 | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | Φ12 × 200 |
| PB-14-250 | 12 | 0.65 | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | Φ14 × 250 |
| PB-16-300 | 15 | 0.74 | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | Φ16 × 240 |
| PB-18-300 | 18 | 0.95 | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | Φ18 × 300 |
| PB-20-350 | 22 | 1.25 | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | Φ20 × 350 |
| Material Type | Corrosion Resistance | Mechanical Strength | Cost | Suitable Environment | Service Life |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot-dip Galvanized Steel | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | Medium | General Outdoor | 20-30 years |
| Stainless Steel 304 | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | Higher | Coastal, Industrial | 30-50 years |
| Stainless Steel 316 | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | High | High Salt Spray | 40-60 years |
| Epoxy Coated Steel | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | Medium | Industrial Pollution | 25-35 years |
| Aluminum Alloy | ★★★★★ | ★★☆☆☆ | Higher | Light Load | 20-30 years |
Wire rod is uncoiled from coil stock, straightened through straightening machines, and precisely cut to specified lengths. This step ensures raw materials have good straightness and dimensional accuracy, laying the foundation for subsequent processing.
Under room temperature conditions, steel is formed into the basic shape of pigtail bolts through mold forging. Cold forging refines grain structure and increases material density, resulting in mechanical properties and fatigue strength superior to machined products.
Special bending molds are used to bend one end of the bolt into the designed "pigtail" shape. Bending angle, radius, and transition curves are all optimized to ensure the bent section has good mechanical properties and does not become a stress weak point.
Threads are processed on the bolt shaft through rolling or cutting methods. Rolling maintains material fiber flow without interruption, thus achieving higher fatigue strength. Thread size and precision should comply with relevant standard requirements.
Bolts undergo quenching and tempering heat treatment to achieve ideal comprehensive mechanical properties. Heat-treated bolts should reach specified hardness and strength indicators, ensuring they can withstand design loads.
Hot-dip galvanizing process is used for anti-corrosion treatment of bolts. According to ISO 1461 standards, zinc coating thickness should meet requirements to ensure good corrosion resistance under various environmental conditions.
Finished products undergo comprehensive quality inspection including visual inspection, dimensional measurement, mechanical performance testing, and salt spray testing. Qualified products are packaged with anti-rust treatment and prepared for shipment.
As critical components of power infrastructure, pigtail bolts need to comply with multiple international and regional standards. Understanding these standards is essential for product selection and quality management.
| Standard Number | Standard Name | Scope of Application | Main Test Items |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF C 33-042 | French LV Insulated Cable Standard | France and French-speaking regions | Mechanical properties, Weather resistance |
| EN 50-483 | European Overhead Line Hardware Standard | EU member states | Dimensional accuracy, Load capacity |
| IEC 61854 | Overhead Lines - Equipment & Accessories | IEC member countries | Comprehensive performance testing |
| ASTM A153 | Hot-Dip Galvanizing Standard for Iron Hardware | USA and North America | Coating thickness, Uniformity |
| ISO 1461 | Hot-Dip Galvanized Coatings Standard | International standard | Appearance, Thickness, Adhesion |
Pigtail bolt products manufactured by Jera Line are tested according to strict quality control standards. Main test items include:
Quality Certification: Jera Line has a complete in-house laboratory that conducts quality inspections throughout daily production, ensuring products meet all requirements for overhead electrical line component standards. Our products have passed multiple international certifications with guaranteed quality.
The main difference between pigtail bolts and regular eye bolts lies in the curved end design:
Pigtail bolts and pigtail screw hooks are essentially very similar, with main differences in end design:
Determining appropriate pigtail bolt specifications requires considering the following factors:
It is recommended to consult technical professionals or suppliers during selection to ensure selected products meet project requirements.
Common anti-corrosion treatments for pigtail bolts include:
Selection of anti-corrosion treatment should be based on specific environmental conditions and service life requirements. For general outdoor power line applications, hot-dip galvanizing is the most common and cost-effective choice.
Pigtail bolts can theoretically be reused, but the following conditions must be met:
Note that reused pigtail bolts should be used with reduced safety factors, with increased inspection frequency after installation. For critical structural locations, new pigtail bolts are recommended to ensure safety.
Safety precautions during pigtail bolt installation:
Common methods to check pigtail bolt installation:
Common causes of pigtail bolt failure:
Service life of pigtail bolts depends on multiple factors:
It is recommended to comprehensively evaluate based on project requirements and environmental conditions, referencing manufacturer-provided product life data combined with regular inspection results.
Storage and transportation recommendations for pigtail bolts:
Pigtail bolts are typically used with the following hardware:
When used together, ensure component specifications match and installation methods comply with design requirements.
Precautions when customizing pigtail bolts:
Among numerous pigtail bolt suppliers, Jera Line has become the preferred partner for more and more customers due to the following core advantages:
Exceptional Quality
Strictly following industry standards to ensure every product meets highest quality requirements
Precision Engineering
Every bolt is precisely engineered for perfect fit and reliable performance
Custom Solutions
Various sizes, load capacities, and thread options to meet your specific project needs
Global Service
Products exported to 50+ countries with extensive experience and comprehensive service network
Our professional technical team is ready to provide you with free consultation services
Get a Quote NowPigtail bolts serve as critical fasteners in power line and telecom infrastructure, with their selection, installation, and maintenance directly affecting the safety and reliability of entire systems. Through this comprehensive guide, we believe you now have a thorough understanding of pigtail bolt design characteristics, technical specifications, application scenarios, and best practices.
When selecting and using pigtail bolts, please always keep the following key points in mind: First, select appropriate specifications and materials based on actual load requirements and environmental conditions; second, strictly follow installation guidelines to ensure installation quality; third, establish regular maintenance and inspection systems to promptly detect and address potential issues.
If you are looking for high-quality pigtail bolts for your projects, Jera Line will be your trustworthy partner. We have more than 10 years of experience in power hardware manufacturing, with products verified by markets globally for quality and service.